CET1171 Lecture #2 - Electricity and Electrostatic Discharge
Materials: Lecture Only Lecture OnlyObjectives:  The student will understand the basics of electricity, The student will understand the basics of electricity, The nature of static electricity, The nature of static electricity, The nature of Electrostatic Discharge (ESD), The nature of Electrostatic Discharge (ESD), How the prevent ESD damage to IBM PC. How the prevent ESD damage to IBM PC.Competency: Competency: The student will become familiar with the core concepts of electricity and static electricity and electrostatic discharge (ESD). The student will learn how to prevent ESD damage to the PC primarily by properly using an anti-static wrist strap. |
Procedures
-
It helps to define electricity in general before proceeding to define static electricity and electrostatic discharge or ESD.
Definition: Electricity: the flow or movement of electrons.
-
Electrons generally form a current (flow) through conductors which are materials that offer little resistance to the electrons. Water won't flow through the plastic walls of a pipe, but it will flow through central opening through the pipe. Similarly electrons will not flow through the insulation around a wire but they will flow through the metal of the wire easily. Many metals make excellent conductors of electricity because of their molecular crystalline structure. Electrons can travel through the metal because the outer electron shells of the metal atoms form a very loose "soup" of electrons that wander around not only the nucleus of any particular atom but also around the nuclei of any nearby atoms in the crystal. This is what gives metals their characteristic metallic properties including the "shiny metallic" appearance which is the result of the way these loose outer electrons interact with light photons striking their surface, and imparts all of the other physical characteristics that are peculiar to metals like malleability – the ability to be pulled into wire, ductility – the ability to be bent, stretched or twisted into a particular shape without breaking, etc. It is this loose "soup" of electrons that allows traveling electrons to pour through the wire with so little resistance and it is the lack of this loose soupy cloud of shared electrons in other materials that makes them, generally speaking, poor conductors of electricity.
Electrons flowing through the conductive metal core of a wire
-
Even though a material may be a poor conductor of electricity, that does not mean that it cannot possess a charge.
Definition: A charge is the presence of a non-zero electric potential
-
These extra electrons are not bound in orbits about atomic nuclei. In fact, a poor conductor is quite often an ideal accumulator of just such "free" electrons. Because the speed of light through a solid is still over 80,000 miles per second, such free electrons can be considered in theory to be everywhere or anywhere on the body in which they reside since at this speed an electron could move across the surface of the earth from one side of the equator to the other in less than 1/7th of a second.
-
Another feature of electricity is potential. This is the amount of force pulling (or pushing if you prefer) on the electrons. If this is zero, then the electrons are not moving. And this is the definition of static electricity. But since static means "not moving" and electricity means "moving electrons" then the term static electricity means "not moving moving electrons" or in other words, the term is an oxymoron. Therefore we will use the proper term: static electric potential.
Definition: Static Electric Potential: is an accumulation of electrons held in a body that are not under a difference in potential such that they are not moving. -
Since they are all at rest within the body they are called static. However, this term is used specifically because it implies that the thing that is not moving is certainly capable of it, and static electrons are certainly capable of moving if conditions change in a favorable way.
-
Electrons themselves can be considered to be a form of energy or a fundamental physical package of energy. Moving electrons however, represent power or the ability to perform work over time.
Definition: Work is a force acting on an object that causes it to be displaced.
-
Fancy language meaning that if a force acts on an object and moves it, then work was done. The amount of work done is the measure of how much mass was moved how far. The physicists will define power as the amount of work done per unit of time.
Definition: Power is the amount of work done per unit of time
-
This simply means that a certain force might move an object one mile so a specific amount of work was done. But one source of this force (energy) might be able to move the object one mile in one hour. The object might be you and the source of this force might be your legs. However, another power source might move you one mile in one minute like the engine of your car. Both do the same amount of work on you, moving you one mile over the surface of the planet, but clearly the car does it much faster and therefore has greater power. So a continuous source of electricity can perform a certain constant amount of work. This can be shown by attaching an electric motor to the electrical power source and in fact this is why it is called a power source because it can cause work to be done steadily over a period of time. The greater the power source, such as wall current versus a battery, the more work it can do within the same time frame.
-
In the case of static electricity, the amount of static electrons in the object collectively form its potential since each one possesses a small electrical charge or voltage just like the poles of a battery. Therefore the actual number of free static electrons in the body form the amount of pull that they will exert on themselves if given a chance.
-
Once this potential gets its opportunity and puts the electrons in motion then they constitute a flow of electricity and moving electrons we have seen can do work and represent power.
-
While at rest, the static charge in the body has no observable effect. But when that object comes in contact with another body, and that body has a different amount of free electrons in it, then the electrons will move to establish an equilibrium in the their distribution through the new body made out of both of the bodies now in contact.
-
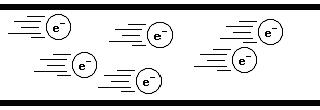
If you have accumulated a considerable number of free electrons as you scuff your rubber soles on a carpet, then when you touch the doorknob to the room (which has very few free electrons in it), you and the doorknob form a new object in which the knob section has very few electrons in it. The high density of them within you makes you electronegative, and all of the electrons are the same charge so they want to spread out, the doorknob provides them a new place to go to get away from each other and so they move into it.
Static electrons gathering on a body over time.
-
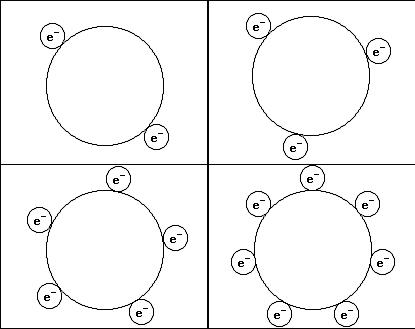
As the electrons accumulate in the body, they establish equilibrium amongst themselves. They are all carrying the same charge and like charges repel. As a result of this as new free electrons arrive on the body they all adjust positions so that they are all evenly spaced from their neighbors so that all of the repulsion forces between each other are the same.
-
Moving electrons we saw earlier are called electricity, and moving electrons represent current. Current does work and has power. This sudden movement of the formerly static electrons from within you and into the doorknob is called an electrostatic discharge and it forms a brief current and it has power. For you to feel the spark caused by an ESD from your own fingertips requires it to have a potential of over 2000 volts. Anything less and you won't even feel it (nor hear it). This means that every time you touch something and an ESD takes place that is perhaps 200 Volts then you will definitely not feel it, but it did happen. Furthermore, there is no way for you to know if and when these events happen (in either direction, by the way.)
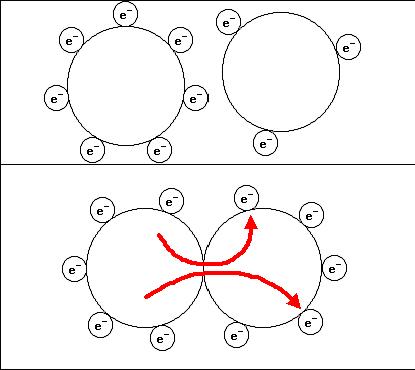
Two bodies with different numbers of free electrons come into contact the electrons move to equidistant positions across the surface of the new body
-
Two bodies with different populations of static or free electrons approach each other. As they make contact they form a new body and the distribution of electrons on the new composite body is uneven. The electrons adjust to a new position of equilibrium in which they are again evenly spaced on the new composite body. In adjusting positions some move from one of the original bodies to the other. This movement of electrons represents power and is electrostatic discharge. This ESD is what can damage an electronic component when the electrons are moving from your fingertips into the chip on the computer component.
-
Modern BIOS chips are programmed with 27 volts, so the ESD from your fingertips can very easily exceed this amount of potential and you would not notice it. And therefore if you touch the chip or a wire trace on the motherboard that leads to it, the ESD from your fingertips can easily program the BIOS chip, unfortunately your voltage is not under control, it is flying across the wires out of control, at random, and it will, of course, program the BIOS chip at random and therefore destroy it. Worse: a CMOS chip runs on a miniscule fraction of a Watt (the unit of measurement for power) usually measured in microwatts. Your fingertip can easily destroy it leaving the PC incapable of booting up because of CMOS configuration errors (because the chip is damaged.)
-
This power can and does damage computer circuitry which is why measures must be taken to avoid destroying components by touching them while carrying a static charge. The PC industry estimates that over 2 billion dollars worth of components are destroyed each year by ESD from people handling components without taking proper precautions to prevent it. The truth of the matter is that almost no users and very few technicians ever take proper ESD measures. The sad part about it is that an anti-static wrist strap costs as little a five dollars and is so easy to use.
Latent damage to a microscopic conductive pathway within an integrated circuit. Though damaged a small bridge still exists, so the circuit continues to function ... for a while.
-
ESD causes two types of electronic component damage: Catastrophic and Latent. Catastrophic damage has occurred when the component has been immediately rendered inoperative by the ESD. The ESD has passed through the IC - Integrated Circuit, chip and burned microscopic circuit components within it so that it no longer functions or has burned a short circuit path so that the electrons no longer flow through the intended pathway within the chip. In latent damage, a pathway has been damaged but a remnant of it remains so that the circuit continues to function normally and appears to be undamaged. However, the damaged pathway is almost always very narrow which increases resistance at the point of damage. This point will continue to overheat when in use due to the increase in the resistance at this narrowed point then cool while not in use. This heating and cooling of the narrow damaged point will continue until it completely breaks, causing the chip to fail.
-
Latent damage can leave a component crippled for hours to months and is extremely difficult to diagnose because of this. This does not mean that the careless technician did not cause the damage and destroy the component, it only means that the careless technician's destruction is difficult to trace back to the lack of proper component handling. As professionals in the PC industry it is your responsibility to protect the client's equipment and even more importantly their data from destruction especially by your own hands. I have heard technicians claim to have worked on PC's for years having never taken ESD precautions and having never caused any damage. The fact of the matter is that they do not understand ESD, or latent damage or they would never try to make this claim. I would like to believe that my student's will not join them in ignorance. The only one that will ever appreciate your efforts is yourself: take pride in your work. Oh, all of the component manufacturers who honor 2 billion dollars worth of ESD damaged merchandise returns will appreciate your efforts too. And this of course will lead to even better prices than they are already.
-
ESD is easily prevented by first being aware of it and second understanding a few basic principles of electricity. The very basic principle of electricity, that it is electrons moving under the force of a potential has already been discussed along with the concepts of energy, work and power in electricity and the nature of static electricity and electrostatic discharge.
-
There is actually no way to prevent ESD, but there is a way to prevent an electrostatic discharge into a sensitive computer component that would damage it. Quite simply the technician must completely discharge into something that will not be damaged by the discharge. Once all of the free electrons have been removed, the technician can then safely handle any ESD sensitive component without damaging it.
-
There is one excellent target into which anything can safely discharge all excess electrons: the Earth. It turns out that the Earth has an affinity for stray electrons, or it might be better stated that the free electrons have an affinity to go into the Earth. The Earth can be, for all practical purposes, considered an infinitely deep well into which electrons will always flow if given the opportunity to do so.
-
If a metal stake is driven into the ground then a technician could touch this and all resident static electrons in his body would discharge harmlessly into the Earth. However, this Earth ground is not always easily available. It can be made available anywhere by running a wire from this stake to wherever the ground is needed.
-
This is done in the modern electrical wiring of buildings. The middle prong of a three prong outlet provides a connection to Earth ground somewhere under the building – or it is supposed to do this. Earth ground is considered to be the "–" or negative side of any potential. Remember that potential is measured in volts, so connecting the "+" lead of a battery to a light bulb and then to Earth ground will work just as well as bringing the other lead from the bulb back to the negative pole of the battery. So the "+" lead of the battery can be thought of as the source of the electrons flowing out of it and the earth ground can be thought of as the recipient of the flow. Electrons will always pour out of any "+" and push through the circuit to reach ground.
-
The three wires from the wall outlet are connected to the computer system’s power supply through the standard computer power cord. So the ground is brought into the computer. The power supply connects it to the case of the computer so that any bare metal surface of the entire case will provide ground: a place for static electrons to be discharged away to ground.
-
Friction between highly dielectric substances such as scuffing ones rubber sole shoes across a synthetic fiber carpet will free many electrons from both the synthetic fibers and the rubber both of which are very highly dielectric substances. In general, good conductors have low dielectric properties and good insulators have high dielectric properties. The dielectric property that concerns us is the ability to hold or release a large quantity of static electrons. Another environmental condition that helps the build up of static electrons is low humidity. Since water vapor molecules have a propensity to pick up static electrons and carry them away.
-
Now in what kind of environment are most of the worlds PC’s? Offices full of synthetic fiber carpets and air conditioners that dramatically reduce the humdity. Ideal conditions for the build up and release of electrostatic discharges.
-
The anti-static wrist strap is a very inexpensive and easy tool to acquire and use at all times. Once the case cover of the PC has been removed the technician should immediately put the anti-static wrist strap on. It does not have to be tight, just in contact with the skin. Anti-static wrist straps have a small wire usually with an alligator clip on the far end from the wrist strap. This should be clipped onto the bare metal of the case which as explained earlier is attached to Earth ground through the power supply through the power cord through the connection in the outlet through the wiring of the building to the Earth.
-
The anti-static wrist strap does have a 1 MegOhm resistor within it to reduce the impact of a shock should power get shorted to the case instead of ground. This is exceedingly rare, in most cases when a bare power line touches the case, the case is usually grounded so that the power simply drains to the ground. This by the way, is a short circuit, when power is running unrestricted or unused straight to ground. When this happens remember that the Earth has an infinite propensity for absorbing them so the flow goes wildly out of control and so many electrons are moving so fast that the wires heat up and melt and can burn insulation and start a fire. You will quickly be aware of a short when working on a PC, it is accompanied by sparking or hissing sounds, the smell of burning insulation or chips and the circuit breaker or fuses will heat and cutoff power to the outlet. Regardless of all of this, the resistor within the anti-static wrist strap is there to protect the technician from being badly shocked.

Typical anti-static wrist strap, most are less than ten dollars.
-
Obviously the technician is not in control of the wiring of the building or the outlet but it can be tested. Outlet wiring testers are another inexpensive tool that can quickly and easily ascertain if the outlet has good Earth ground. Once this is tested, the ground of the case as long as the system is plugged in and turned off can be trusted.


Typical outlet checker or tester. Most are less than ten dollars.
-
Having the proper tools is obviously paramount to being able to work on the PC, which starts with practicing the proper anti-static protocol, fortunately the above tools are very inexpensive. The outlet tester images were taken from an online retailer asking $9.99 and and the anti-static wrist strap was selling for $4.95 The beginning PC repair technician should have both, but only the anti-static wrist strap will be required for participation in the class.
-
Proper ESD Protocol for working on the AT class system:
1. Check the outlet for proper wiring, especially proper ground, using an outlet tester. 2. Plug in the system to establish contact with the ground provided by the outlet. 3. Be sure that the system is turned off - connecting or disconnecting internal components while the system is on can destroy the component and/or the motherboard. 4. Remove the case cover. 5. Remove jewelry, tie back long hair, roll up long sleeves. 6. Put on the anti-static wrist strap. 7. Attach the alligator clip to any bare metal edge of the case. 8. Proceed to work on the system... -
The power supply physically connects the center power cord line carrying the Earth ground to its outer casing which is in turn directly attached to the entire computer chassis thereby grounding the entire case. However, the case is NOT grounded and not suitable for safely discharging yourself to ground if it is not attached to ground. It is attached to ground through the power cord which in turn is attached to a properly wired outlet.
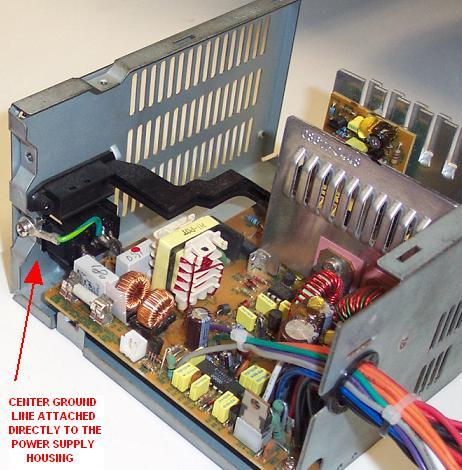
Power supply with cover removed showing physical connection of power cord center (ground) line to its housing which in turn comes into comtact with the case, thus grounding the entire chassis
Review Questions
-
An electron can be considered a small physical package or quantity of ______________.
-
Moving electrons represent ______________ because they can perform _____________ over time.
-
Each electron holds a small electrical _____________ Since they are all the same this makes them all _____________ each other.
-
Static electrons are _____________ electrons in a body that are not _____________.
-
Static electrons in a body position themselves at ______________ distances from each other, thus arriving at _______________.
-
When two bodies come in contact with different numbers of static electrons in them the
electrons ______________ from the body with the larger number to the body with the smaller
number reestablishing _______________.
-
This movement of electrons from the body with the excess to the body with the deficiency
when they come in contact is called _______________________________.
-
One body that has an infinite capacity to absorb stray electrons is the ________________.
-
_________________ is provided in modern electrical outlets from the middle hole of the three prong outlet.
-
Electricity will flow from the positive pole of a battery to any point connected to _____________.
-
If the outlet is correctly wired to ground, then the power cord brings ground to the
computer system's ________________________.
-
The computer system's power supply attaches ground to the entire _____________.
-
Name two environmental conditions common to the places where computers are most commonly used that encourage the build up of static electricity.
-
What two inexpensive and easily used tools should the technician have in order to ensure that computer components will not be damaged by ESD?
-
As long the wall outlet is wired properly and the system is ________________ in and
_______________ off then the case will provide ground.
-
As soon as the computer case cover has been removed the technician should put on the
__________________________ and clip it to any bare metal surface of the system's
______________________
-
The industry manufacturers estimate that at least _____________________ dollars worth of returned computer components have been returned because they have been damaged by ESD.
-
The anti-static wrist strap contains a ________________ resistor to prevent a bad
electric shock in the case of a _______________ circuit or faulty outlet wiring.
-
The best defense against being shocked by a system plugged into an outlet that is wired
wrong is to use an ___________________ on the outlet first.
-
The total number of free electrons that have gathered in a body represent the total
_______________ that will act on them when given the chance.
-
The larger the difference between free electrons in two bodies that come into contact,
the larger the _______________ of them that will move into the deficient body when they make contact.
-
The average minimum potential in an electrostatic discharge that is required in order to
be felt by a human is roughly ___________________ volts.
-
The BIOS EEPROM chip is reprogrammed with _______ volts, an amount much smaller than what can be felt by a human during an electrostatic discharge.
-
The CMOS RAM chip built into the motherboard runs on ___________________ an extremely small amount of power that can easily be delivered from a human fingertip in an ESD.
-
Describe the two types of ESD damage that improperly grounded technician’s can do to computer circuitry.
-
Insulators have excellent ________________ properties one of the aspects of these
properties is that they easily accumulate ________________ electrons.
-
List two common materials found in the normal computer environment with high dielectric properties.
-
List and describe four physical properties of metals that are the direct result of the way the outer electron shells of the metal crystal allow electrons to wander between atoms forming a loose electron "soup":
-
______________ is the measure of a force acting on a body that causes it to be displaced or moved.
-
______________ is the rate at which work is performed. This is why batteries or the wall
outlet are referred to as _______________ sources.
Copyright©2000-2007 Brian Robinson ALL RIGHTS RESERVED